What is Skin Pigmentation?
Depending on the culture, skin colour and tone can have different meanings and importance. All individuals have an inherent skin colour and type but environmental factors – especially UV exposure – play a major part in the change of one’s skin colour/tone over time.
However, pigmentation conditions (dyschromia) where there is an abnormal accumulation of pigmentation, can be a cause of stress, anxiety and even severe health implications (skin cancer). Here we will discuss only cosmetic pigmentation disorders (hyperpigmentations).
Melanin is the main substance in the skin that is responsible for skin colour. The melanin molecules are present inside small pockets called melanosomes produced by melanocytes. The melanin present in the skin is the main source responsible for human skin colour. The activity and interaction with skin cells (keratinocytes) account for differing skin colour and skin types in varying ethnicities.
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition that occurs when patches of skin become darker than the surrounding skin due to an excess of melanin production. It can affect people of all ages, genders, and skin types. It can also affect any part of the body, including the face, arms, hands, and legs. The treatment process of how to get rid of pigmentation on skin involves different modalities.
What Causes Pigmentation On Skin?
There are several skin pigmentation causes, including sun damage, hormonal changes, genetics, inflammation, medications, and skin injuries. Excessive sun exposure is a major cause of hyperpigmentation, as it triggers the production of melanin in the skin.
Hormonal changes, especially those that occur during pregnancy or menopause, can also be the cause of pigmentation on skin. Certain medications, such as antibiotics, can also cause black or red pigmentation on skin as a side effect.
The main sign of pigmentation is the presence of dark patches or spots on the skin. These spots can vary in size, shape, and colour intensity. They may be flat or raised, and they may or may not be itchy or painful. In some cases, pigmentation may be accompanied by other skin symptoms, such as dryness, flaking, or redness. If your skin is severely dehydrated, we recommend speaking with our aesthetician regarding skin dehydration treatment.

Types of Skin Pigmentation Disorders
Skin pigmentation is usually diagnosed based on a visual examination of the affected skin. The first step in treating pigmentation is identifying the type. Skin analysis devices with special light can allow additional visualisation of some pigmentations. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other skin conditions. Once the type has been identified, your dermatologist can recommend effective pigmentation treatment in Singapore.
Melasma
Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation that is caused by hormonal changes and typically occurs on the face. It is more common in women than in men, and it often develops in women of childbearing age. It is a chronic condition and difficult to treat.
Solar Lentigos
These lesions are more common in men of older age and usually are flat and round. Sizes can vary and are commonly seen on the face and back of hands. UV radiation is usually the main cause.
Freckles (Ephelises)
Freckles are small, flat, circular spots that appear on the skin, usually in areas exposed to sunlight. They are most commonly found on the face (upper cheeks, nose), arms, and shoulders. Freckles are usually harmless and are more commonly seen in fair-skinned individuals. They can vary in size, colour, and density and tend to darken with sun exposure.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
This is a type of hyperpigmentation that develops after a type of inflammation (acne, eczema, sunburn) or skin injury. It can also occur after a type of energy-based device (IPL, laser, etc). It is more common in people with darker skin tones.
Types of Skin Pigmentation Treatments Available in Singapore
Complete “cure/removal” of hyperpigmentation is theoretically and empirically not possible since melanin will always be part of the skin, but with proper preventive measures and treatment, they can be improved. Recurrence of hyperpigmentations can occur after treatments in the clinic and is dependent on multiple factors. Proper application of sunscreen when outdoors and sun avoidance habits are essential in the treatment of skin pigmentation as well as a major part of how to prevent skin pigmentation.
Over-the-counter and prescription topical skin pigmentation creams and ointments containing cysteamine, niacinamide, hydroquinone, retinoids, or kojic acid may be used to lighten dark spots and even out skin tone.

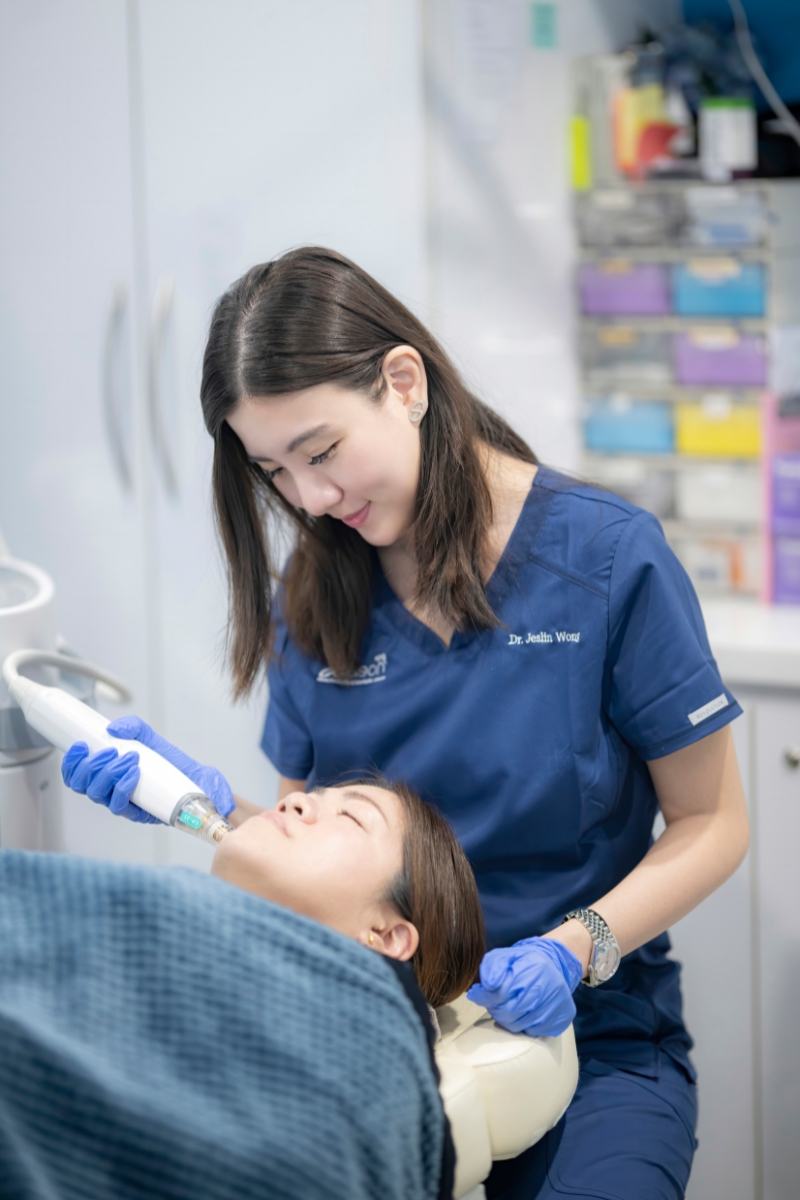
Find the right doctor for skin pigmentation treatment in singapore
Finding the right specialist for hyperpigmentation treatment is key to achieving an even, radiant complexion. With Dr Jeslin’s years of experience, you can be assured that Aeon Medical will come up with an effective treatment plan for lightening of hyperpigmentation.
By customising treatment plans based on individual needs and using several technologies, we can effectively improve your skin pigmentation issues in Singapore. Book an appointment with us today!
Disclaimer
The information provided on this website is for educational purposes only and is, in no way, intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. We make no representation or warranty of any kind regarding the accuracy, availability, adequacy, or validity of the information or procedures outlined on the website. Always consult professional medical and aesthetic advice for your skincare and medical concerns.
References:
- "Skin Pigmentation Disorders", National Library of Medicine, https://medlineplus.gov/skinpigmentationdisorders.html
- Amin Mahmood Thawabteh, Alaa Jibreen, Donia Karaman, Alà Thawabteh, and Rafik Karaman, "Skin Pigmentation Types, Causes and Treatment—A Review", National Library of Medicine, National Center for Biotechnology Information, 2023, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10304091/
- Seemal R. Desai, MD, FAAD, "Hyperpigmentation Therapy: A Review", National Library of Medicine, National Center for Biotechnology Information, 2014, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4142815/
Contact Us
Talk to our friendly AEON team by filling out the form. We will get back to you within 2-3 working days. For a faster response, contact our hotline below.
Call us anytime
Address
9 Scotts Rd, #06-01/02/03 Scotts Medical Centre, Pacific Plaza Singapore 228210
